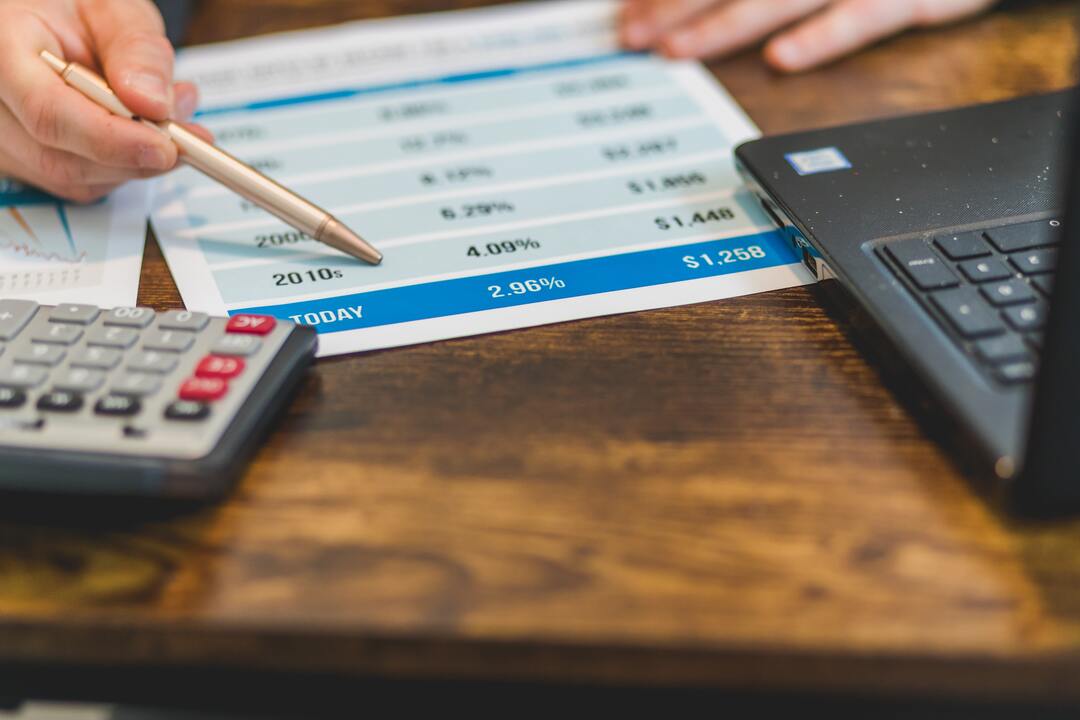
What is an interest rate?
An interest rate is an amount charged by a lender to a borrower for the use of money or an asset. It is typically expressed as a percentage of the total amount borrowed or invested over a specific period, such as a year. Interest rates are a crucial component of the global financial system and impact various aspects of the economy, including savings, borrowing, investment, and spending.
In general, interest rates serve two primary purposes. First, they compensate lenders for the risk and opportunity cost associated with lending money. When individuals or organizations lend money, they are foregoing the opportunity to use that money for other purposes, such as investing or spending. Interest rates ensure that lenders are adequately compensated for the use of their funds.
Second, interest rates incentivize borrowing and discourage saving. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more attractive as the cost of borrowing decreases. This can stimulate economic activity by encouraging individuals and organizations to invest in new projects, purchase goods and services, and make other forms of investments. Conversely, when interest rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, and saving becomes more attractive. This can discourage spending and investment and can potentially slow down economic activity.
Interest rates can be set by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank in the European Union. Central banks use interest rates as a tool to manage inflation and stabilize the economy. When inflation is too high, central banks may raise interest rates to reduce borrowing and spending and slow down economic activity. Conversely, when the economy is in a recession or experiencing slow growth, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending and encourage economic activity.
Interest rates can also vary based on the type of loan or investment. For example, credit cards and personal loans typically have higher interest rates than mortgages and auto loans due to the increased risk associated with these forms of borrowing. Similarly, savings accounts and certificates of deposit typically offer lower interest rates than riskier investments, such as stocks or bonds.
How does an interest rate affect businesses?
Interest rates can have a significant impact on businesses, both positively and negatively, depending on the circumstances. Here are some ways in which interest rates affect businesses:
Cost of borrowing: The interest rate determines the cost of borrowing money. When interest rates are high, it becomes more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which can discourage investment and growth. Conversely, when interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, and businesses may be more willing to invest in new projects.
Investment decisions: Interest rates can influence the investment decisions of businesses. When interest rates are high, businesses may be more likely to invest in low-risk, short-term projects with quick returns, whereas when interest rates are low, businesses may be more willing to invest in long-term projects with higher risk but potentially higher returns.
Consumer spending: Interest rates can also impact consumer spending, which can affect businesses that rely on consumer demand. When interest rates are high, consumers may be less likely to spend money, as they will have to pay more in interest on any loans or credit cards they use. This can result in reduced sales for businesses that sell consumer goods or services. Conversely, when interest rates are low, consumers may be more likely to spend money, which can increase demand for businesses.
Exchange rates: Interest rates can impact exchange rates, which can affect businesses that operate in international markets. When interest rates rise, the currency of the country in question may appreciate in value, which can make exports more expensive and reduce demand for businesses that rely on exports. Whereas, when interest rates fall, the currency may depreciate, which can make exports cheaper and increase demand for businesses that export.
Cash flow: Higher interest rates can impact a business’s cash flow. If a business has outstanding loans or debts with variable interest rates, a rise in interest rates can increase the monthly payments, reducing cash flow available for other purposes. This can lead to a strain on cash flow, making it more challenging to invest in growth opportunities or cover operating expenses.
Conclusion
Interest rates can have a significant impact on businesses, affecting their borrowing costs, cash flow, and investment decisions. The impact of interest rates on businesses depends on various factors, including the type of business, the industry it operates in, and the economic conditions. As such, businesses need to stay informed about interest rate changes and develop strategies to manage their finances effectively.
Interest rates can have a significant impact on businesses, and it is important for business owners and managers to keep an eye on interest rate trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.